12 Best Bootable USB Flash DriveCreation Tools / Software
Bootable USB drive creation tools to install new operating system from USB. Prepare the pen drive for single operating system or multiple OS on single USB. You can also save user files along side of the bootable partition. Its 2017 and no one uses the traditional DVD.
Most of the Linux OS would be tested by creating a ‘Live’ disk which gives, complete experience of the full operating system without installing anything on your hard disk.
Windows 7, 8.1 and now Windows 10 can be easily installed from bootable USB. If your mother board is comparatively new, you may have to deal with the UEFI or the legacy BIOS if your computer is not that new. Both way, you can easily create bootable USB drive using all of the listed software here.
1. Rufus
Rufus is a simple and easy to use. It automatically detects your USB flash drive and capacity so you can easily identify which device you are formatting. The bootable USB drive can be created for newer hardware supporting UEFI or for legacy BIOS. You only have to select proper options from the list.
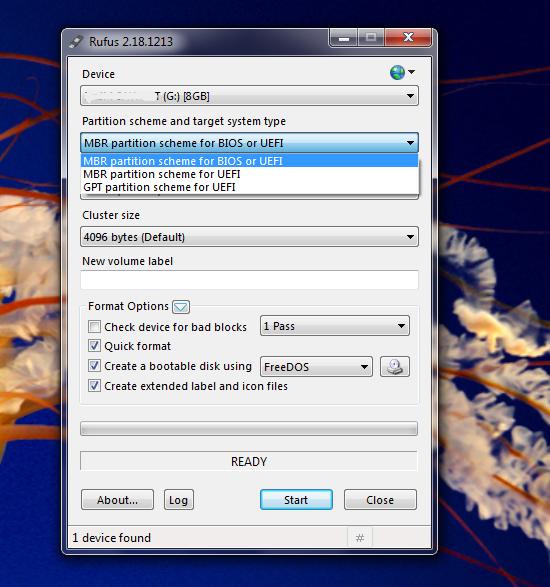
Steps to create bootable flash drive
The type bootable USB drive you are creating depends on motherboard you are using.
For Old Motherboards Using Legacy BIOS
➤ First select the ISO image file, from the disk icon behind 'create a bootable disk using' option. ( Do this first only because, if you select other options firs, and the file later, the settings go to default after selecting the ISO file. May be a bug )
Select the target drive and file system (For Windows keep it NTFS).
➤ Select 'MBR partition scheme for BIOS or UEFI' from partition scheme and target system type.
➤ Keep the file system, cluster size as it is or you can change it to NTFS for Windows and exFAT for Linux.
➤ You can give appropriate name to the resulting bootable drive.
➤ ISO image on your hard disk must be a valid bootable image because Rufus scan the image before you load it.
➤ Click start button and wait for the process to complete. This may take up to 20 minutes.
For New Motherboards Using UEFI
➤ UEFI motherboards most of the time need 64 bit Windows. Else you will get 'Could not locate '\dfi\boot\bootx64.efi: [14] Not found' error. If you get this error, you must need 64 bit Windows version. The 7th generation Intel CPU do not support Windows 7 or older. You must have Windows 10.
➤ Select the ISO image file of OS you want burn.
➤ Select 'GPT partition scheme for UEFI' from partition scheme and target system type.
➤ NTFS as file system .
If you create bootable USB using MBR scheme, you may get an error like 'Windows can not be installed. The partition is GPT type.
Carefully check the options as above before you hit the start button.
💧 Download Rufus
2. WinToBootic
Again a basic tool with minimum option. Just drag and drop your .ISO image or click on ‘drop ISO here’ icon.
It will auto detect your USB media.
Hit the ‘Do It’ button, WinToBootic will do the everything rest.
+ minimal interface, run without installation.
- Does not support Linux
💧 Download WinToBootic
3. RMPrepUSB
It's all in one tool. Features come with cluttered interface. If you don't know what are you doing, don't use it. I personally do not recommend it if you want a simple bootable USB to install new operating system.
RMPrepUBS is specialized in creating multiple partition in a single USB drive. You can install multiple ISO of different OS or save user files along side of the bootable USB.
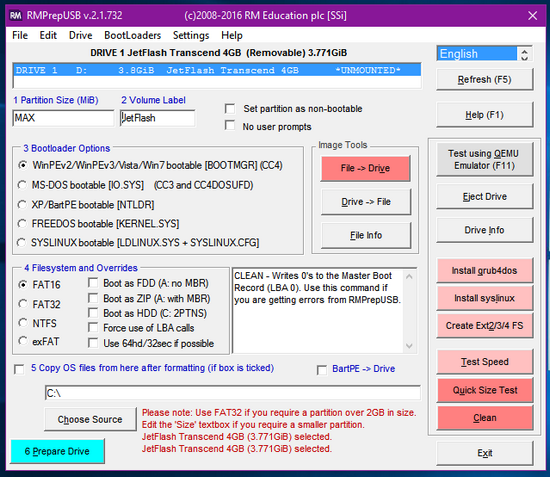 The special feature of RMPrepUSB is you can create a partition in USB drive just like you do on your hard disk making it more useful for saving files plus using the same drive as a separate folder for storing files.
The special feature of RMPrepUSB is you can create a partition in USB drive just like you do on your hard disk making it more useful for saving files plus using the same drive as a separate folder for storing files.
This keeps your files separate from the operating system files.
For advanced users.
Difficult to use
Create ISO from USB drive.
Edit the hard drive grub or syslinux boot loader.
Test speed of the USB drive.
Support all OS.
💧 Download RMPrepUSB
4. Universal USB Installer
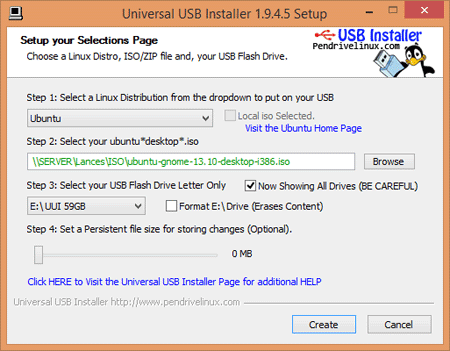 Specialized tool for creating bootable live Linux OS. It has predefined list of most of the Linux distributions available. Give path of ISO image and USB flash drive you want to boot from. Prepare a Live antivirus rescue disk using it. A special option for this is also given for reuse CD.
Specialized tool for creating bootable live Linux OS. It has predefined list of most of the Linux distributions available. Give path of ISO image and USB flash drive you want to boot from. Prepare a Live antivirus rescue disk using it. A special option for this is also given for reuse CD.
+ Specialized menu for Linux, also support Window 7
💧 Download Universal USB Installer
5. YUMI
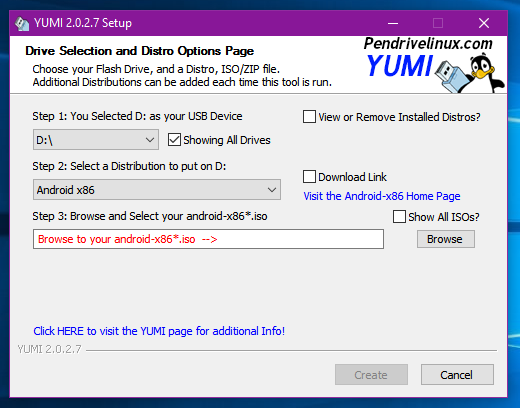 You can download the ISO of your favorite OS. YUMI have large collection of free OS based on Linux and other free OS projects. Just select what you want and YUMI will give you the direct download link for it.
You can download the ISO of your favorite OS. YUMI have large collection of free OS based on Linux and other free OS projects. Just select what you want and YUMI will give you the direct download link for it.
The interface is quite easy to use and useful.
💧 Download YUMI
6. UNetbootin
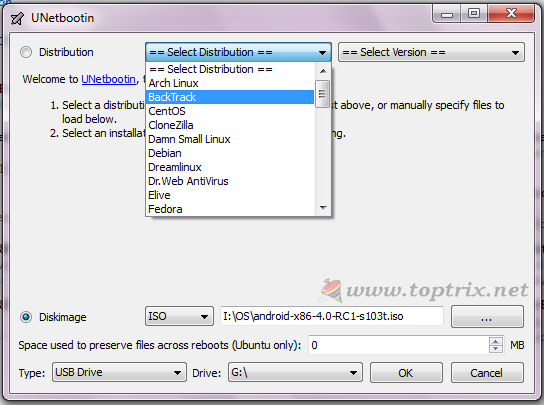 This tool is an exact clone of Universal USB installer or you can also say Universal USB installer is a clone of UNetbootin.
This tool is an exact clone of Universal USB installer or you can also say Universal USB installer is a clone of UNetbootin.
Create a bootable USB for any Linux distribution.
If you are not using Windows as your host operating system, then UNetbootin is an option to go for. UNetbootin is available for Linux, iOS and Windows.
So if you are using Linux, most of the software's listed here will not run where UNetbootin will come to help.
💧 Download UNetbootin
7. Linux Live USB Creator (LiLi)
LiLi is one more software used to make bootable USB. The special feature called built-in Vitalization allow users to run the installed Linux operating system without restarting the Windows which are an exclusive feature of LiLi.
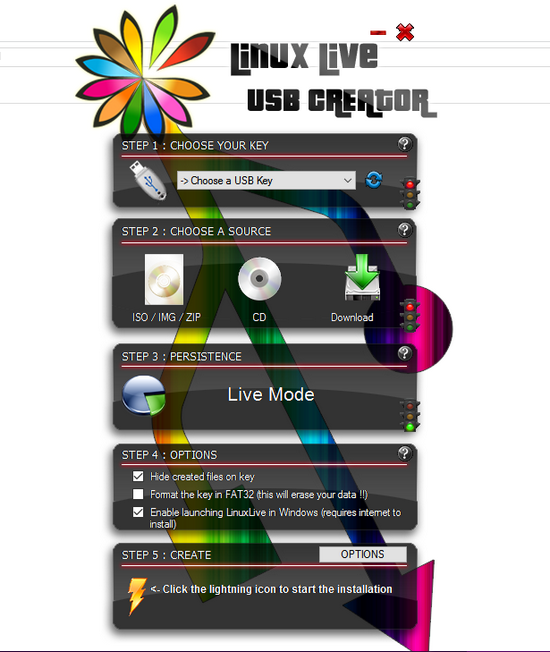
If you are concerned only about Linux you must go for this.
💧Download LiLi Creator
8. WinSetUp From USB
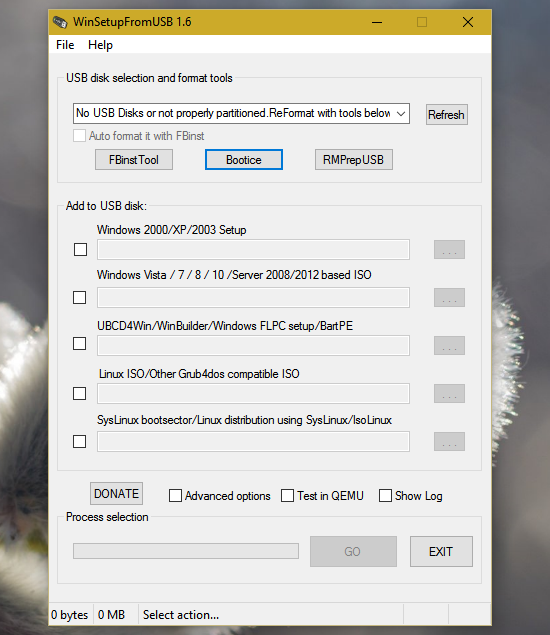
This is also a tool for those who want to install multiple operating system on one USB device.
WinSetup From USB let you install Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 2000, Windows 7, Windows 10, any Linux distribution.
When you prepare the USB drive using ‘WinSetup From USB’ you will be presented with the list of operating systems installed on the thumb drive and select the preferred operating system to boot from.
Though the interface is simple, non expert users may find it difficult to use.
💧Download WinSetUp From USB
9. WinUSB Maker
This is more that just a bootable USB creation tool, though you can use it for that also. This is a special tool that will allow you to clone hard disk partition on your portable memory device like USB thumb drive or portable hard disk.
WinUSB maker copies exact partition of your local hard disk along with the boot files and file structure. You can also restore the saved partition from the USB device to your hard disk making it useful as a backup tool. This is a must have tool for everyone. We have already discussed about this earlier here.
💧 Download WinUSB Maker
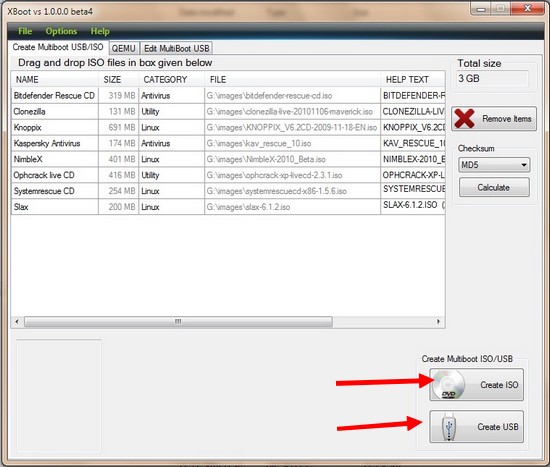
10. XBoot
This is more than just a bootable USB maker. You can create a rescue CD or a disk having multiple operating systems or tools like antivirus rescue CD. It combines multiple tools in ISO image making it more useful than just a USB creating tool. XBoot can create ISO image from files and then write these files to USB drive for booting or installation.
 💧 Download XBoot here
💧 Download XBoot here
11. Windows Bootable Image Creator
This is a straight forward and ultra small tool that accomplishes its job as you expect. It has a super simple interface and minimum buttons to avoid confusion of new users. This is a tool from AskVG.
There are only basic buttons and only one task to do. Just create a bootable USB driveto install or try new operating systems. I wonder how it is so small and light. It is just 160KB in size.
💧 Download Windows Bootable Image Creator
12. Other Tools
➤There are other tools like Novicorp WinToFlash, Passcape ISO Burner, Windows official USB disc creation tool, Ubuntu startup disc creator and Flash Boot.
➤Novicorp WinToFlash is also a tool that will help you to recover deleted boot loader apart from creating a bootable flash drive.
➤Passcape ISO burner is also a simple and small utility to create bootable USB drive.
Windows official USB creation tool is an official tool to create a bootable USB drive to install downloaded Windows 7 and Windows 8 ISO images without burning it to traditional discs.
➤The Ubuntu start up disc is also a tool for Linux fan boys.
➤FlashBoot is a bit tool having around 24 MB is download size. It has more options than any other tool, but is actually a paid tool, but anyone can use it for free.
➤If you want to try out Google Chromium Operating system, you have to use a recommended open source tool Image Writer for Windows. It is also a small but useful too without any garbage features. A simple and straight tool.
Verdict:
⏩ 'Rufus' is best of everybody.
⏩ 'LiLi' is the best choice for Linux specialists.
⏩ 'WinSetup From USB' is for installing multiple OS in one USB drive.
⏩ 'RMPrep USB' is for making partition in USB drive along with Windows.
⏩ If you want to clone a complete partition with OS 'WinUSB Maker' is the best choice.
The USB drive is Easy to create, erase and reuse. Can install multiple OS on same USB at a time. Faster booting and installation speed. Portable and easy to handle.Preparing the Bootable USB drive is easy and straightforward. These 12 software can make your device ready within 5 minutes and 2 clicks.
Most of the Linux OS would be tested by creating a ‘Live’ disk which gives, complete experience of the full operating system without installing anything on your hard disk.
Windows 7, 8.1 and now Windows 10 can be easily installed from bootable USB. If your mother board is comparatively new, you may have to deal with the UEFI or the legacy BIOS if your computer is not that new. Both way, you can easily create bootable USB drive using all of the listed software here.
1. Rufus
Rufus is a simple and easy to use. It automatically detects your USB flash drive and capacity so you can easily identify which device you are formatting. The bootable USB drive can be created for newer hardware supporting UEFI or for legacy BIOS. You only have to select proper options from the list.

Steps to create bootable flash drive
The type bootable USB drive you are creating depends on motherboard you are using.
For Old Motherboards Using Legacy BIOS
➤ First select the ISO image file, from the disk icon behind 'create a bootable disk using' option. ( Do this first only because, if you select other options firs, and the file later, the settings go to default after selecting the ISO file. May be a bug )
Select the target drive and file system (For Windows keep it NTFS).
➤ Select 'MBR partition scheme for BIOS or UEFI' from partition scheme and target system type.
➤ Keep the file system, cluster size as it is or you can change it to NTFS for Windows and exFAT for Linux.
➤ You can give appropriate name to the resulting bootable drive.
➤ ISO image on your hard disk must be a valid bootable image because Rufus scan the image before you load it.
➤ Click start button and wait for the process to complete. This may take up to 20 minutes.
For New Motherboards Using UEFI
➤ UEFI motherboards most of the time need 64 bit Windows. Else you will get 'Could not locate '\dfi\boot\bootx64.efi: [14] Not found' error. If you get this error, you must need 64 bit Windows version. The 7th generation Intel CPU do not support Windows 7 or older. You must have Windows 10.
➤ Select the ISO image file of OS you want burn.
➤ Select 'GPT partition scheme for UEFI' from partition scheme and target system type.
➤ NTFS as file system .
If you create bootable USB using MBR scheme, you may get an error like 'Windows can not be installed. The partition is GPT type.
Carefully check the options as above before you hit the start button.
💧 Download Rufus
2. WinToBootic
Again a basic tool with minimum option. Just drag and drop your .ISO image or click on ‘drop ISO here’ icon.
It will auto detect your USB media.
Hit the ‘Do It’ button, WinToBootic will do the everything rest.
+ minimal interface, run without installation.
- Does not support Linux
💧 Download WinToBootic
3. RMPrepUSB
It's all in one tool. Features come with cluttered interface. If you don't know what are you doing, don't use it. I personally do not recommend it if you want a simple bootable USB to install new operating system.
RMPrepUBS is specialized in creating multiple partition in a single USB drive. You can install multiple ISO of different OS or save user files along side of the bootable USB.

This keeps your files separate from the operating system files.
For advanced users.
Difficult to use
Create ISO from USB drive.
Edit the hard drive grub or syslinux boot loader.
Test speed of the USB drive.
Support all OS.
💧 Download RMPrepUSB
4. Universal USB Installer

+ Specialized menu for Linux, also support Window 7
💧 Download Universal USB Installer
5. YUMI
Yumi, short for Your Universal Multiboot Installer. YUMI allow you to prepare the bootable USBdrive multiple operating system in one USB drive without formatting it.

The interface is quite easy to use and useful.
💧 Download YUMI
6. UNetbootin

Create a bootable USB for any Linux distribution.
If you are not using Windows as your host operating system, then UNetbootin is an option to go for. UNetbootin is available for Linux, iOS and Windows.
So if you are using Linux, most of the software's listed here will not run where UNetbootin will come to help.
💧 Download UNetbootin
7. Linux Live USB Creator (LiLi)
LiLi is one more software used to make bootable USB. The special feature called built-in Vitalization allow users to run the installed Linux operating system without restarting the Windows which are an exclusive feature of LiLi.

If you are concerned only about Linux you must go for this.
💧Download LiLi Creator
8. WinSetUp From USB

This is also a tool for those who want to install multiple operating system on one USB device.
WinSetup From USB let you install Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 2000, Windows 7, Windows 10, any Linux distribution.
When you prepare the USB drive using ‘WinSetup From USB’ you will be presented with the list of operating systems installed on the thumb drive and select the preferred operating system to boot from.
Though the interface is simple, non expert users may find it difficult to use.
💧Download WinSetUp From USB
9. WinUSB Maker
This is more that just a bootable USB creation tool, though you can use it for that also. This is a special tool that will allow you to clone hard disk partition on your portable memory device like USB thumb drive or portable hard disk.

WinUSB maker copies exact partition of your local hard disk along with the boot files and file structure. You can also restore the saved partition from the USB device to your hard disk making it useful as a backup tool. This is a must have tool for everyone. We have already discussed about this earlier here.
💧 Download WinUSB Maker
10. XBoot
This is more than just a bootable USB maker. You can create a rescue CD or a disk having multiple operating systems or tools like antivirus rescue CD. It combines multiple tools in ISO image making it more useful than just a USB creating tool. XBoot can create ISO image from files and then write these files to USB drive for booting or installation.

11. Windows Bootable Image Creator
This is a straight forward and ultra small tool that accomplishes its job as you expect. It has a super simple interface and minimum buttons to avoid confusion of new users. This is a tool from AskVG.
There are only basic buttons and only one task to do. Just create a bootable USB driveto install or try new operating systems. I wonder how it is so small and light. It is just 160KB in size.
💧 Download Windows Bootable Image Creator
12. Other Tools
➤There are other tools like Novicorp WinToFlash, Passcape ISO Burner, Windows official USB disc creation tool, Ubuntu startup disc creator and Flash Boot.
➤Novicorp WinToFlash is also a tool that will help you to recover deleted boot loader apart from creating a bootable flash drive.
➤Passcape ISO burner is also a simple and small utility to create bootable USB drive.
Windows official USB creation tool is an official tool to create a bootable USB drive to install downloaded Windows 7 and Windows 8 ISO images without burning it to traditional discs.
➤The Ubuntu start up disc is also a tool for Linux fan boys.
➤FlashBoot is a bit tool having around 24 MB is download size. It has more options than any other tool, but is actually a paid tool, but anyone can use it for free.
➤If you want to try out Google Chromium Operating system, you have to use a recommended open source tool Image Writer for Windows. It is also a small but useful too without any garbage features. A simple and straight tool.
Verdict:
⏩ 'Rufus' is best of everybody.
⏩ 'LiLi' is the best choice for Linux specialists.
⏩ 'WinSetup From USB' is for installing multiple OS in one USB drive.
⏩ 'RMPrep USB' is for making partition in USB drive along with Windows.
⏩ If you want to clone a complete partition with OS 'WinUSB Maker' is the best choice.